What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a serious infection of a woman’s reproductive organs. PID is a leading cause of infertility in the United States. At least 1 million cases of PID occur annually in the United States. Following PID, scarring will cause approximately 20 percent of women to become infertile, 18 percent to develop chronic pelvic pain, and 9 percent to have ectopic pregnancies. PID can also lead to life-threatening complications.
What Causes PID?
 The most common causes of PID are the two sexually transmitted diseases, chlamydia and gonorrhea. PID occurs when an infection in the genital tract isn’t treated right away. The infection spreads from the cervix up into the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. PID can develop anywhere from several days to several months after infection with an STD. PID can cause scarring in the fallopian tubes, which can lead to tubal pregnancy (a life-threatening pregnancy in which there is no chance of producing a baby).
The most common causes of PID are the two sexually transmitted diseases, chlamydia and gonorrhea. PID occurs when an infection in the genital tract isn’t treated right away. The infection spreads from the cervix up into the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. PID can develop anywhere from several days to several months after infection with an STD. PID can cause scarring in the fallopian tubes, which can lead to tubal pregnancy (a life-threatening pregnancy in which there is no chance of producing a baby).
A woman who has had PID may have problems getting pregnant or be unable to have children at all. PID can also cause long-lasting pain. Some women have no symptoms or symptoms too mild to notice. However, PID can cause permanent damage even when it is completely painless. PID does not cause endometriosis, as asked by a reader.
Symptoms
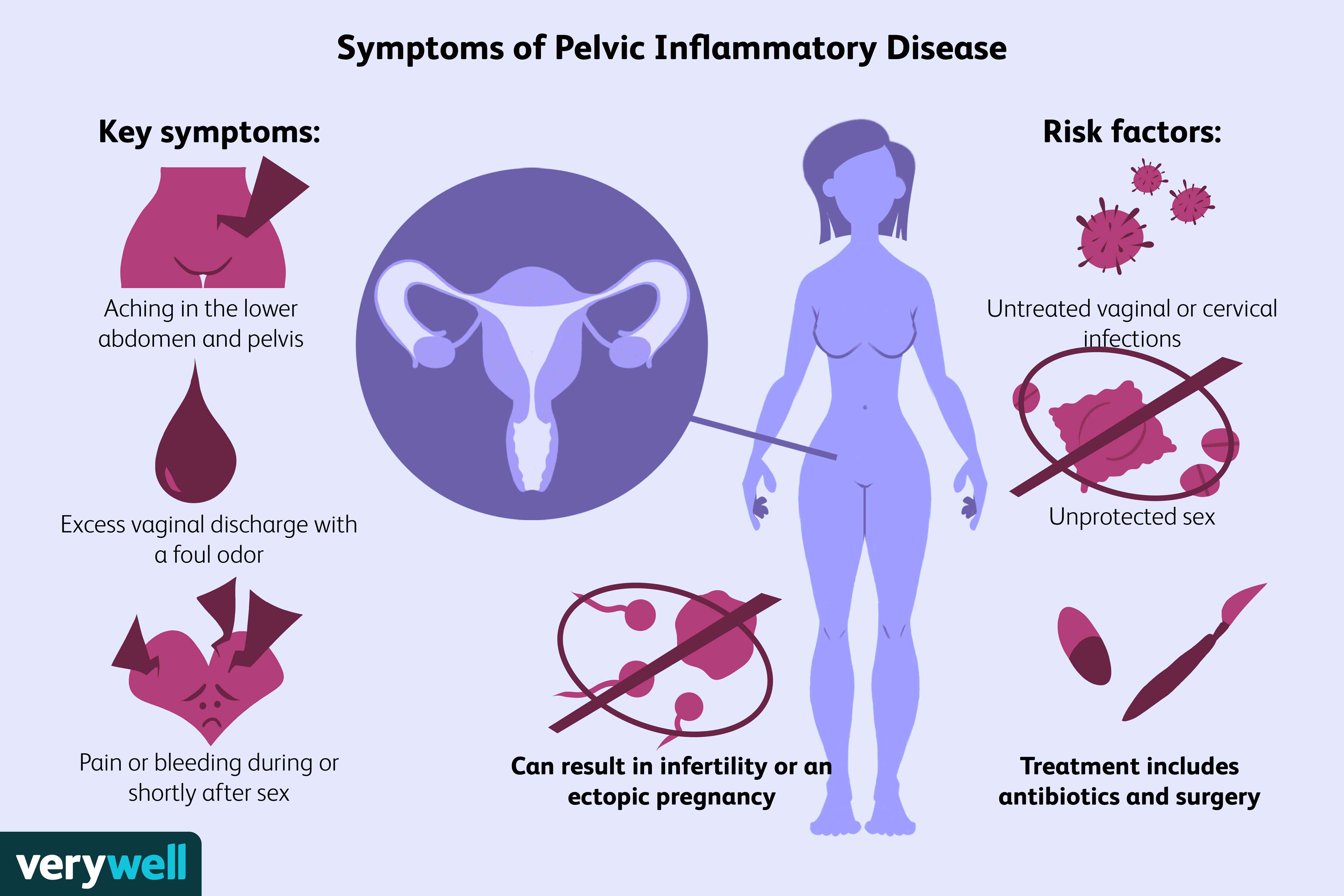
The symptoms of PID are:
- pain or tenderness in the lower abdomen
- pain during sexual intercourse
- bleeding between menstrual periods
- increased or changed vaginal discharge
- nausea and/or vomiting
- fever and chills
Incubation Period
It varies. Can be months, even years after the infection of an STD.
Treatment
If PID is diagnosed, the woman and all sex partners must be treated. Otherwise, they will continue to pass the infection back and forth. Avoid sex, or use condoms and spermicide during sex, until all sex partners are completely cured. After treatment, go back for a follow-up exam with your health care provider or clinic to be sure PID is eliminated.
Prevention
The best way to prevent PID is to prevent sexually transmitted diseases. If you are sexually active, get tested for chlamydia and gonorrhea at least once a year. If you think you may have an STD, get tested and treated right away, before the infection spreads. To prevent STDs use a latex condom and spermicide every time you have sexual intercourse.
Did You Know:
At least 1 million cases of PID occur annually in the United States. Of all infertile women, at least 15 percent are infertile because of tubal damage caused by PID.
Following PID, scarring will cause approximately 20 percent of women to become infertile, 18 percent to develop chronic pelvic pain, and 9 percent to have ectopic pregnancies.
Can Men Help Prevent PID?
Yes, Yes, Yes! Men are more likely than women to have symptoms from chlamydia or gonorrhea, the infections that often cause PID, so they will often know before a woman. These symptoms include:
- pus-like discharge from the penis – often yellowish in color
- pain or burning with urination
 A man can help protect his female partner(s) by telling her at once if he is diagnosed with an infection. Early treatment can spare her lasting damage to her body. Men should be treated with antibiotics to cure chlamydia or gonorrhea. Men should take all the medicine prescribed, even if symptoms go away. Avoid sex, or use condoms with a spermicide for sex until sex partners are completely cured. All partners must be treated to stop the cycle of infection.
A man can help protect his female partner(s) by telling her at once if he is diagnosed with an infection. Early treatment can spare her lasting damage to her body. Men should be treated with antibiotics to cure chlamydia or gonorrhea. Men should take all the medicine prescribed, even if symptoms go away. Avoid sex, or use condoms with a spermicide for sex until sex partners are completely cured. All partners must be treated to stop the cycle of infection.
The Best Way To Prevent PID is To Prevent STDs!
To prevent PIDs:
- Don’t have sexual intercourse (Abstinence)
- Use a condom & spermicide – Always & Every time!
- Limit number of partners (The more people you have sex with, the greater your risk of getting an STD. If your partner has sex with others, you are also at risk.)
- Get Tested!
- Get Treated!